BS 8674:2025 fire risk assessor competence is now clearly defined for the first time. When a nursing home owner appoints a fire risk assessor, how can they be confident that the assessor has the skills to evaluate their complex, high-risk building? This new British Standard provides a nationally recognised framework that defines competence in assessing fire risk, ensuring that the complexity of a building matches the assessor’s capability.
Published by the British Standards Institution (BSI) in August 2025, this standard addresses a critical gap exposed by the 2017 Grenfell Tower tragedy and subsequent regulatory reforms. This guide explains what BS 8674 means for Irish fire safety professionals, how it relates to existing Irish legislation, and why it matters for anyone responsible for fire safety in buildings.
What is BS 8674:2025 Fire Risk Assessor Competence Standard?
BS 8674:2025, titled “Built Environment – Framework for Competence of Individual Fire Risk Assessors – Code of Practice”, provides a structured framework for assessing the competence of individual fire risk assessors working in the built environment. Developed through extensive industry collaboration led by the Fire Sector Confederation, this standard establishes performance-based criteria to determine whether someone is suitably competent to conduct fire risk assessments.
Key Features of the Standard
- Three progressive competence levels (Foundation, Intermediate, Advanced)
- Clear criteria for knowledge, skills, and professional behaviours
- Matching of assessor capability to building complexity
- Framework for third-party verification and certification
Important: BS 8674 does not prescribe how to conduct a fire risk assessment. That guidance is covered by standards such as PAS 79-1:2020 and BS 9792:2025. Instead, BS 8674 defines who is competent to conduct assessments based on knowledge, experience, skills, and professional behaviours.
BS 8674:2025 Fire Risk Assessor Competence: Why It Matters for Ireland
While BS 8674:2025 is a UK standard, it provides valuable guidance for Irish fire safety professionals who currently operate without a formal tiered competence framework. Irish legislation requires fire risk assessments to be conducted by “competent persons,” but it does not define structured competence levels for varying building complexities.
BS 8674 fills this gap by offering Irish fire risk assessors:
- A best-practice framework to demonstrate capability
- Particularly valuable when working with complex or high-risk buildings such as nursing homes, hospitals, and multi-occupancy residential premises
- Cross-border consistency for companies working in both jurisdictions
- Assurance to insurers and clients that assessors possess appropriate qualifications
Many Irish fire safety professionals already reference UK standards such as PAS 79-1:2020 for fire risk assessment methodology, and BS 8674 serves as a complementary competence benchmark.
Fire Risk Assessor Competence Levels in BS 8674:2025
The standard establishes three progressive competence levels, each aligned with building complexity and fire risk:
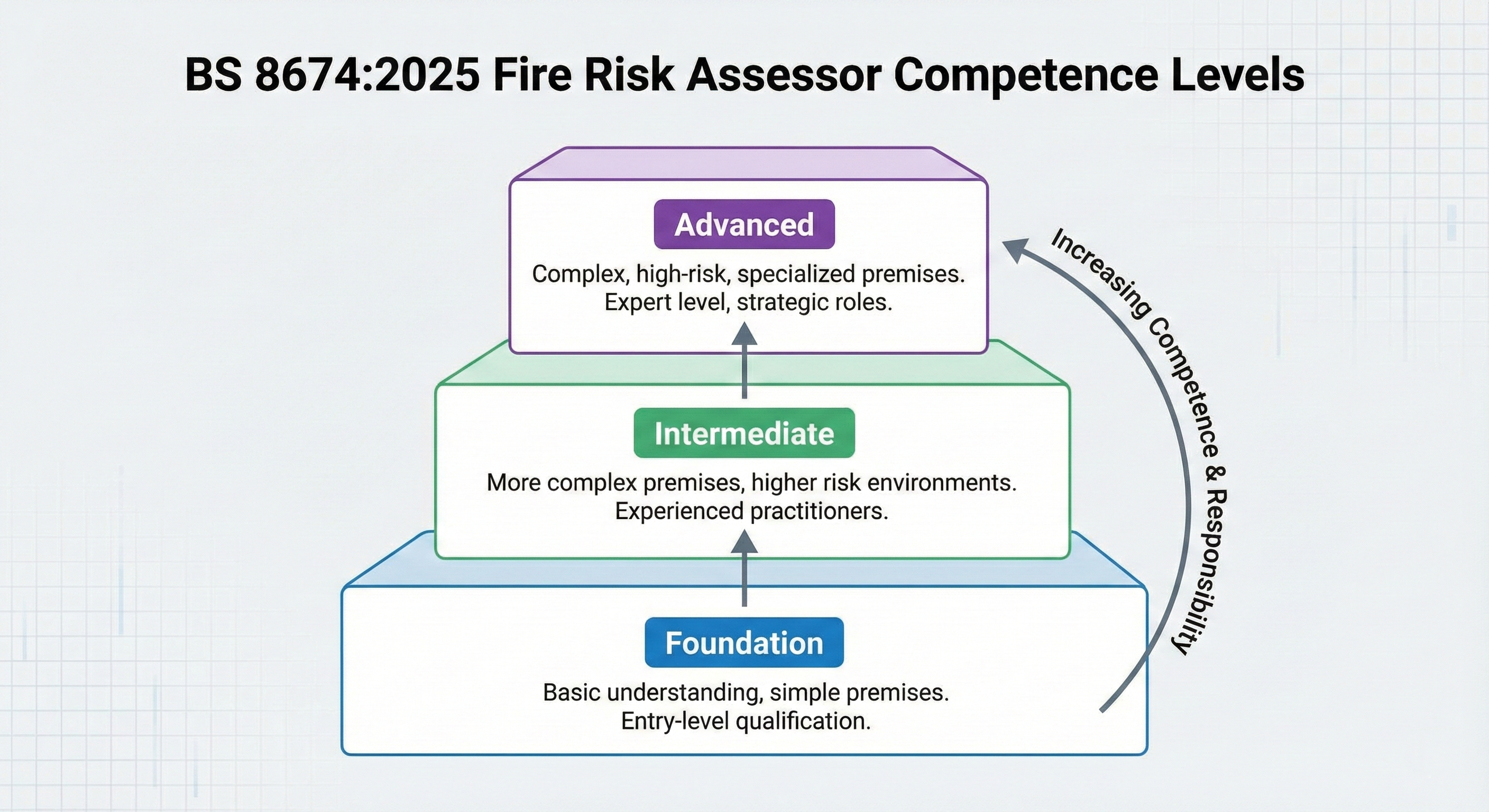
Entry-Level Assessors
Designed for new entrants to the profession and those assessing simple, low-risk premises. Suitable building types include small offices, retail shops, and straightforward commercial premises with limited occupancy and uncomplicated layouts. Foundation-level assessors possess fundamental knowledge of fire safety principles and can identify basic hazards, but their scope is deliberately limited to environments where fire risk is well-controlled and building design is relatively simple.
Experienced Assessors
For assessors with greater experience handling medium-complexity buildings. This level encompasses public venues, mid-rise residential properties, and premises with moderate fire risk and more complex fire safety systems. Intermediate assessors demonstrate deeper understanding of fire dynamics, building construction, and the interaction between active and passive fire protection measures.
Senior Professionals
Reserved for highly experienced professionals working in complex, high-risk environments. Building types at this level include large residential blocks, nursing homes, hospitals, multi-occupancy buildings, high-rise structures, and premises requiring sophisticated risk analysis. Advanced assessors possess comprehensive knowledge of fire engineering principles, building regulations, and emergency management in vulnerable occupancy scenarios.
Competence Level Comparison
| Risk Profile | Example Premises | Required Competence Level |
|---|---|---|
| Low Risk | Simple offices, standard occupancy, straightforward fire safety measures | Foundation |
| Moderate Risk | Public buildings, mid-rise residential, complex occupancy or fire safety systems | Intermediate |
| High Risk | Hospitals, nursing homes, high-rise buildings, vulnerable occupants, intricate fire safety strategies | Advanced |
This matching principle ensures buildings receive appropriate scrutiny from assessors with suitable expertise for the complexity and risk involved.
What BS 8674:2025 Competence Framework Covers
✅ The Standard Includes
BS 8674 outlines comprehensive requirements for fire risk assessor competence across five key areas:
- Knowledge requirements covering understanding of building construction, use, occupancy characteristics, and relevant fire safety legislation
- Skills encompassing the ability to evaluate fire risk through systematic analysis, identify fire hazards, and assess the adequacy of existing fire prevention and protection measures
- Documentation interpretation including previous fire risk assessments, maintenance records, and building plans
- Professional behaviours and ethical standards ensuring assessors operate with integrity, objectivity, and accountability
- Communication skills to present findings clearly and provide practical, proportionate recommendations
❌ The Standard Excludes
BS 8674 explicitly does not cover several specialist areas:
- Fire risk appraisals of external wall constructions (addressed by PAS 9980:2022)
- Assessments requiring destructive inspection or invasive testing
- Fire engineering services, calculations, or the design, testing, and maintenance of fire protection systems
- Organisational competence (BS 8674 applies to individual assessors only)
- Specialist environments such as nuclear facilities, offshore installations, and other unique high-hazard premises
Irish Fire Safety Legislation
Several key pieces of legislation govern fire safety in Ireland:
⚖️ Fire Services Acts 1981 and 2003
The Fire Services Acts 1981 and 2003 comprise the primary legislation governing fire safety in buildings. Section 18(2) places a duty of care on “every person having control over premises” to take all reasonable measures to guard against fire outbreaks, provide reasonable fire safety measures and procedures, and ensure the safety of persons in the event of fire.
⚖️ Safety, Health and Welfare at Work Act 2005
The Safety, Health and Welfare at Work Act 2005 requires employers to ensure workplace safety, including fire risks. Section 19 requires comprehensive risk assessments that include fire safety considerations.
⚖️ Building Regulations and Building Control Acts
The Building Regulations 1997 to 2021 set out detailed requirements for fire safety in building design in Technical Guidance Document B (TGD-B). The Building Control Acts 1990 and 2007 require Fire Safety Certificates for new buildings and significant alterations.
Competence Requirements in Irish Law
While Irish legislation requires that fire risk assessments be conducted by “competent persons”, there is currently no formal Irish standard or framework that defines competence across levels.
This absence of a structured competence framework means:
- Determining assessor competence is left largely to professional judgment
- Duty holders must independently verify an assessor’s qualifications and experience
- There is no nationally agreed benchmark for matching assessor capability to building complexity
- Professional bodies and certification schemes operate without a unified competence standard
BS 8674 provides the structured, measurable framework that Irish legislation currently lacks. It offers Irish fire risk assessors a voluntary mechanism to demonstrate their capability and helps duty holders verify that assessors possess appropriate qualifications for specific building types.
The UK Legal Context
BS 8674:2025 directly supports compliance with the Building Safety Act 2022, which requires that individuals appointed to conduct fire risk assessments be competent. The standard provides measurable, verifiable benchmarks for this competence.
The standard aligns with broader regulatory reforms following Grenfell, including:
- Fire Safety Act 2021
- Fire Safety (England) Regulations 2022
- BS 8670-1:2024 (competency framework for building safety professionals)
“BS 8674:2025 marks a significant step forward in the collective effort to make buildings safer for residents.”
— Alex Norris, Minister for Building Safety and Fire“The standard gives all stakeholders confidence that competence can now be clearly demonstrated against a professional framework capable of independent verification.”
— Dennis Davis, Competence Director at the Fire Sector ConfederationWho Benefits from BS 8674:2025 Fire Risk Assessor Competence?
For Fire Risk Assessors
- A clear career progression pathway from Foundation to Advanced levels
- A benchmark for seeking certification or professional recognition from bodies such as IFSM or IFE
- Clarity on which building types match their competence level
For Responsible Persons and Duty Holders
- Confidence that assessors have appropriate qualifications for specific buildings
- A reference standard for verifying assessor credentials before appointment
- Support for legal compliance under Irish and UK legislation
- Assurance of quality and consistency in fire risk assessments
For Professional Bodies and Certification Schemes
- A framework for validating member competence and establishing membership criteria
- Guidance for continuing professional development (CPD) requirements
- A reference for third-party verification schemes
- Objective criteria for competence audits and membership renewals
For Training Providers
- Clear competence requirements for curriculum development
- Support for learners transitioning into professional roles
- Measurable learning outcomes at each competence level
- Recognition of qualifications across different jurisdictions
The Future of Fire Risk Assessor Competence
BS 8674:2025 represents a fundamental shift toward the professionalisation of fire risk assessment in the UK and Ireland. The UK government has signalled its intention to require independent third-party certification of fire risk assessor competence, making BS 8674 a likely foundation for future professional regulation.
By establishing transparent, measurable competence criteria, the standard:
- Reduces variability in assessor qualifications across the industry
- Enhances public safety through consistent, quality assessments
- Supports career development and professional recognition
- Lays the groundwork for potential regulatory requirements
- Improves accountability throughout the building lifecycle
While Ireland has not yet adopted a formal competence framework equivalent to BS 8674, the standard provides valuable guidance for those seeking to demonstrate their capability. As professional standards evolve globally, frameworks like BS 8674 may influence future Irish policy development in this area.
BS 8674:2025 Fire Risk Assessor Competence FAQs
BS 8674:2025 is a British Standard titled “Built Environment – Framework for Competence of Individual Fire Risk Assessors – Code of Practice”. Published by BSI on 15 August 2025, it establishes a national framework for assessing fire risk assessor competence at three levels: Foundation, Intermediate, and Advanced. The standard defines the knowledge, skills, experience, and professional behaviours required at each level.
No. BS 8674 is a UK standard and is not legally mandated in Ireland. However, Irish legislation under the Fire Services Acts 1981 and 2003 requires fire risk assessments to be conducted by “competent persons”. BS 8674 provides a voluntary best-practice framework that Irish fire safety professionals can use to demonstrate their competence, particularly when working with complex buildings or UK-based clients.
Foundation Level: For assessors working in low-risk environments such as small offices, retail shops, and simple commercial premises.
Intermediate Level: For those assessing medium-complexity buildings including public venues, hotels, mid-rise residential properties, and premises with more complex fire safety systems.
Advanced Level: For highly experienced professionals working in complex, high-risk environments such as hospitals, nursing homes, high-rise buildings, and multi-occupancy residential premises with vulnerable occupants.
Nursing homes, hospitals, and healthcare facilities with vulnerable occupants typically require Advanced-level competence. These buildings have complex fire safety requirements, including sleeping accommodation, residents with mobility limitations, sophisticated evacuation strategies, and the need for Personal Emergency Evacuation Plans (PEEPs). HIQA Regulation 28 compliance demands thorough fire safety expertise at this level.
HIQA Regulation 28 (Fire Precautions) requires designated centres to have adequate fire safety arrangements, including competent fire risk assessments. While HIQA does not specifically reference BS 8674, the standard’s Advanced level aligns with the complexity of healthcare facilities. Irish providers can use BS 8674 to demonstrate that their fire risk assessors have appropriate capability for these high-risk environments, supporting HIQA compliance.
They serve different purposes and are complementary:
PAS 79-1:2020 provides guidance on conducting a fire risk assessment, including methodology, process, and documentation requirements.
BS 8674:2025 defines who is competent to conduct assessments – the knowledge, skills, experience, and behaviours required at each level.
A competent assessor uses the PAS 79-1 methodology while meeting the competence criteria in BS 8674.
You can verify competence through several methods:
- Check registration on the National Fire Risk Assessors Register (NFRAR), which uses BS 8674 competence levels
- Verify BAFE SP205 third-party certification for fire risk assessment services
- Check membership of professional bodies such as IFSM (Institute of Fire Safety Managers) or IFE (Institution of Fire Engineers)
- Request evidence of relevant qualifications, experience, and CPD records
- Confirm valid Professional Indemnity and Public Liability insurance
- Ask for examples of previous fire risk assessments on similar building types
Before appointing an assessor, verify:
- Their competence level matches your building’s risk profile (Foundation/Intermediate/Advanced)
- They have specific experience with your building type (especially for nursing homes, hospitals, or high-rise buildings)
- They hold valid Professional Indemnity insurance covering fire risk assessments
- They are registered with a recognised body, such as NFRAR, or hold BAFE SP205 certification
- They can demonstrate ongoing CPD and up-to-date knowledge of current standards
- They follow a recognised methodology such as PAS 79-1:2020
Yes. Several UK-based professional bodies and certification schemes recognise BS 8674 competence levels, and these are open to Irish professionals. The National Fire Risk Assessors Register (NFRAR), administered by the Institute of Fire Safety Managers (IFSM), uses BS 8674 as its competence benchmark. Irish assessors can register at Foundation, Intermediate, or Advanced levels by demonstrating the required knowledge, experience, and professional standards.
No. BS 8674 explicitly excludes fire risk appraisals of external wall constructions. FRAEWs require specialist expertise and are covered by a separate standard: PAS 9980:2022. However, BS 8674 helps ensure that only assessors with appropriate competence (usually Advanced level) undertake or advise on these complex assessments.
BS 8674 applies only to general, non-invasive fire risk assessments. It explicitly excludes:
- Assessments requiring destructive inspection or invasive testing
- Fire engineering services, calculations, or fire safety design
- Design, testing, and maintenance of fire protection systems
- Organisational competence (the standard applies to individuals only)
- Specialist environments such as nuclear facilities and offshore installations
Fire risk assessments should be reviewed regularly and whenever there are significant changes. Irish guidance recommends review:
- At least annually for most premises
- More frequently for high-risk premises such as nursing homes (HIQA may expect 6-monthly reviews)
- After any significant changes to the building, occupancy, or fire safety systems
- Following a fire or near-miss incident
- When new fire safety legislation or guidance is published
The assessor conducting the review should have the appropriate level of competence for the building’s risk profile.
BS 8674 does not mandate specific qualifications but requires assessors to demonstrate appropriate knowledge, skills, and experience. Recognised indicators include:
- Fire safety qualifications such as NEBOSH Fire Certificate, IFE qualifications, or CFPA Europe Diploma
- Registration on NFRAR at the appropriate level
- BAFE SP205 third-party certification
- Membership of professional bodies (IFSM, IFE, IIRSM)
- Degree or diploma in fire engineering or fire safety
- Relevant experience in fire risk assessment for similar building types
- Evidence of ongoing CPD
In the UK, the government has signalled its intention to require independent third-party certification of fire risk assessor competence, making BS 8674 a likely foundation for future professional regulation. In Ireland, there are currently no indications that BS 8674 will become mandatory, but it provides valuable voluntary guidance. As professional standards evolve globally, frameworks like BS 8674 may influence future Irish policy development in this area.
The UK Building Safety Act 2022 requires that individuals appointed to conduct fire risk assessments be competent. BS 8674 directly supports this requirement by providing measurable, verifiable benchmarks for competence. While the Building Safety Act applies in England and Wales (not Ireland), Irish professionals working on UK projects or for UK clients should be aware of these requirements.
Phoenix STS Fire Risk Assessment Services
At Phoenix STS, we recognise the importance of competent, thorough fire risk assessments that align with best practice standards. Our team of qualified fire safety professionals conducts comprehensive PAS 79-2020 Fire Risk Assessments across a wide range of commercial and residential premises throughout Ireland.
For healthcare facilities, we specialise in Nursing Home PAS 79-1 Fire Risk Assessments, with a deep understanding of the unique challenges and regulatory requirements of these vulnerable occupancy environments.
Our approach aligns with the competence principles outlined in BS 8674:2025, ensuring complex buildings receive the required level of scrutiny from appropriately qualified professionals.
Contact Phoenix STSRelated Resources
🎓 Training Courses
📋 Consultancy Services
Disclaimer
This article is provided for general informational and educational purposes only. While every effort has been made to ensure accuracy, this content does not constitute legal, regulatory, or professional advice. Fire safety requirements may vary depending on your specific circumstances, building type, and applicable regulations. Always consult with qualified fire safety professionals and refer to current legislation, including the Fire Services Acts, Safety, Health and Welfare at Work Act 2005, and Technical Guidance Document B, for guidance specific to your facility. The information provided about BS 8674:2025 is based on publicly available sources at the time of writing. Phoenix STS accepts no liability for any actions taken or not taken based on this article.











